Search results
Search for "surface roughening" in Full Text gives 12 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Influence of the epitaxial composition on N-face GaN KOH etch kinetics determined by ICP-OES
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 41–50, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.4

- , surface roughening is an integral part of flip-chip processing. The two approaches towards surface roughening are wet- and dry-chemical etching [11][12]. During wet etching, aqueous KOH and other alkaline or acidic solutions are commonly used to remove GaN from the N-polar surface in an anisotropic manner
Tuning the performance of vanadium redox flow batteries by modifying the structural defects of the carbon felt electrode
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1698–1706, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.165

- scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, it can be seen that the surface morphology of the fibers of both samples looked identical and thus any kind of surface roughening leading to an increase of the surface area can be ignored. This is further supported by our previous study were the BET measurements
Advanced scanning probe lithography using anatase-to-rutile transition to create localized TiO2 nanorods
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 412–418, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.40

- properties of this technique are discussed, it should be excluded that AFM tip-induced growth is not simply a surface roughening effect. In Figure 3, the difference between a scratched film (panel A) and a mechanically broken film (panel B) is demonstrated. The scratched line in Figure 3A is marked yellowish
- growth observable at the breaking line. Nanorods growing around the breaking line might originate from anatase nanoparticles released during the breaking process. Besides surface roughening, charging is another candidate that could promote the growth on scratched regions. The tip causes a lot of friction
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
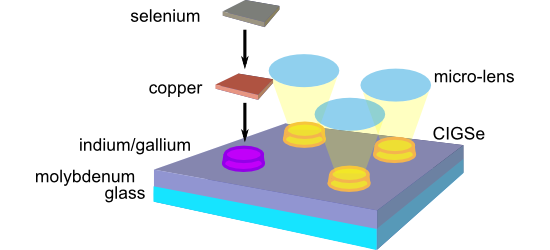
- nucleation can be induced by local surface roughening. Existing indium islands then act as a material sink for further indium adatoms, such that they accumulate material and keep growing as long as further indium is deposited. At the same time, further island nucleation is suppressed in the vicinity of an
- of laser modifications on glass, which were recorded at tilting angles of 0 and 52° with respect to the surface normal, are depicted in Figure 5. Figure 5a shows a laser spot with slight surface roughening that increases towards the center. Using a somewhat higher laser fluence, pronounced laser
Controlling surface morphology and sensitivity of granular and porous silver films for surface-enhanced Raman scattering, SERS
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2813–2831, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.263

- . Altogether this work shows for the first time the effectiveness of a plasma treatment for surface roughening of silver thin films and its profound influence on the interface-controlled SERS enhancement effect. The method can be used for low-cost, large-scale production of SERS substrates. Keywords: plasma
- treatment; silver; sputtering; surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS); surface roughening; Introduction The great enhancement of Raman signals obtained from molecules when they are in close vicinity to a rough noble-metal surface (e.g., gold, silver and copper) has attracted a great deal of interest in
- substrates from simple silver films. Conclusion This systematic study proves the possibility of increasing the surface roughness of sputtered silver films through application of different rf plasma treatments as an alternative to the widely employed method of electrochemical surface roughening of silver
Enhancement of X-ray emission from nanocolloidal gold suspensions under double-pulse excitation
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2609–2617, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.242

- pre-pulse excitation of the solution film. When the pre-pulse energy increases, the main pulse encounters a strongly excited ENZ shell around the gold nanoparticles as well as, at longer delays, surface roughening of the solution film and cavitation bubbles below the surface [47]. Such scenarios are
Light extraction efficiency enhancement of flip-chip blue light-emitting diodes by anodic aluminum oxide
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1602–1612, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.152

- , abbreviated as YAP:Ce) and reduced the total reflection of light via surface roughening. The LEE of the LED was approximately two times that of traditional LEDs [16]. The use of a high-index-contrast photonic crystal [17][18] and colloidal-based microsphere arrays in conventional top-emitting LEDs [19], and
Growth and morphological analysis of segmented AuAg alloy nanowires created by pulsed electrodeposition in ion-track etched membranes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1272–1280, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.131

- electrodeposition of thin films where the effect is called kinetic surface roughening [55][56]. These Au/Ag/Au nanowires constitute excellent platforms for the fabrication of small nanogaps, by selective dissolution of the Ag segment. The method named “on-wire lithography” has been reported previously for wires of
Bright photoluminescence from ordered arrays of SiGe nanowires grown on Si(111)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 2498–2504, doi:10.3762/bjnano.5.259

- the surface roughening of the substrate and the density of defects formed; typically, the emission current used was about 10 pA and the ion dose = 1016 PA/cm2/s. This point is essential to provide an efficient selectivity during the last NW growth step. After the FIB etching, the samples were
Digging gold: keV He+ ion interaction with Au
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 453–460, doi:10.3762/bjnano.4.53

- Figure 2g), as well as the 2D FFTs in Figure 3b). This suggests that the pattern formation is governed by diffusion processes of gold adatoms and surface vacancies. Together with the sputtering processes it leads to surface roughening and the development of a periodic pattern. Although the sputtering
Pure hydrogen low-temperature plasma exposure of HOPG and graphene: Graphane formation?
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 852–859, doi:10.3762/bjnano.3.96

- rougher, and (ii) blisters start to form, which are more pronounced for longer plasma exposures (Figure 2a and Figure 2b). Regarding these AFM measurements, it is clear that both surface roughening and blister formation contribute to D and D' peaks of the Raman spectrum. The surface roughening can neither
- Ef as a result of surface roughening after plasma exposure. After soft annealing (Figure 3b, bottom panel), the secondary peak rises due to the flattening of the layers. The broadening effect is alleviated and the σ peaks reappear at shifted positions at 8.3 and 10.2 eV below Ef. As suggested by the
Friction and durability of virgin and damaged skin with and without skin cream treatment using atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 731–746, doi:10.3762/bjnano.3.83

- skin samples. The reduction is similar to that on the nanoscale, since skin cream is a shear-thinning fluid as mentioned earlier. Figure 9b shows that the coefficient of friction decreases as the normal load increases. Increased surface roughening and a large quantity of wear debris are believed to be
- increased surface roughening and a large quantity of wear debris. The coefficient of friction of pig skin is larger than that of rat skin on the nanoscale. The effect of velocity, normal load, and relative humidity on pig skin has the same trend as that for rat skin both on the nano- and macroscale, as does
















































































































